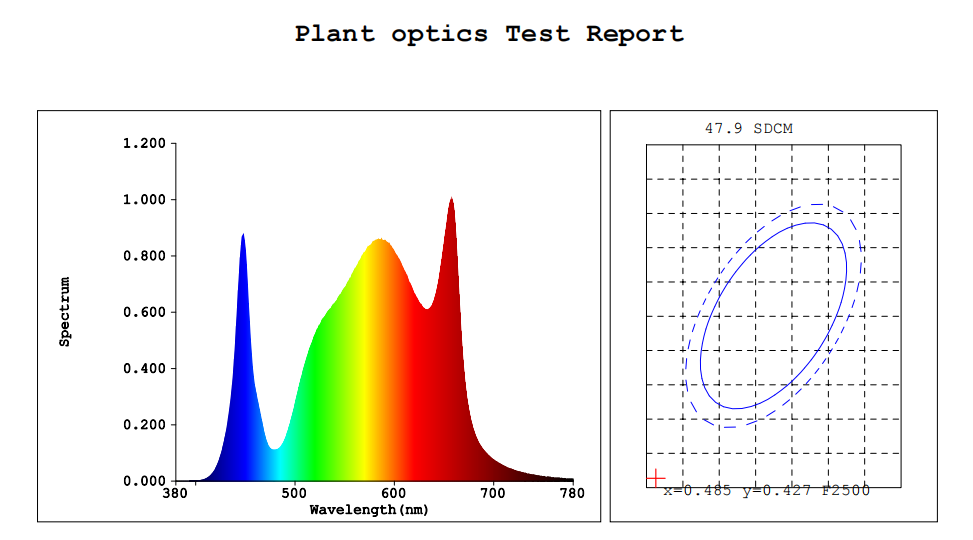
Quality and accumulation level of functional substances are one of the important indicators of facility vegetable production. For vegetables, the main nutritional quality indicators include primary metabolites (sugar, protein, minerals, vitamins, cellulose, etc.) and secondary metabolites (anthocyanins, phenolics, yellows, lycopene, etc.) . These indicators are controlled by lighting conditions, and are nutritional quality indicators that …
More-
Light environment regulation target and quality physiology of artificial light vegetable production
-
Application and Strategy of UV Artificial Light Regulation in Plant Factory
Plant factory UV artificial light control has high application value in achieving high-quality and high-yield facility gardening, but the application dose and irradiation time should be selected according to the crop type and application target to ensure application safety. For the selection of crop types, facilities vegetables, medicinal plants, flowers and fruit trees can all …
More -
Application of UV radiation in plant factories
The quality of facility horticultural crops is an important indicator to measure the commodity value of their products. International research on the nutrition of horticultural products is in the ascendant. The utilization and adjustment of ultraviolet light in plant factories are very important to ensure high quality and high yield. The artificial control of UV …
More -
The regulating effect of UV on the quality of facility plants
Hoffmann et al. (2015) found that PAR intensity plays an important role in the adaptation of plants to UV radiation. Therefore, the special morphological and physiological characteristics affected by strong light are also affected by blue light. The author believes that a larger amount of blue light in the spectrum is beneficial to the ability …
More -
The regulation of UV on the growth and quality of facility plants
Due to the absorption of covering materials in greenhouses and greenhouses, the ultraviolet part of sunlight will be greatly reduced. An important feature of the greenhouse growth system is the lack of mid-wave ultraviolet UV-B (280~320nm) in natural sunlight. The physiological effects of this phenomenon are unclear. Plants often develop a thick leaf epidermis or …
More -
Distribution characteristics of ultraviolet light in plant factories
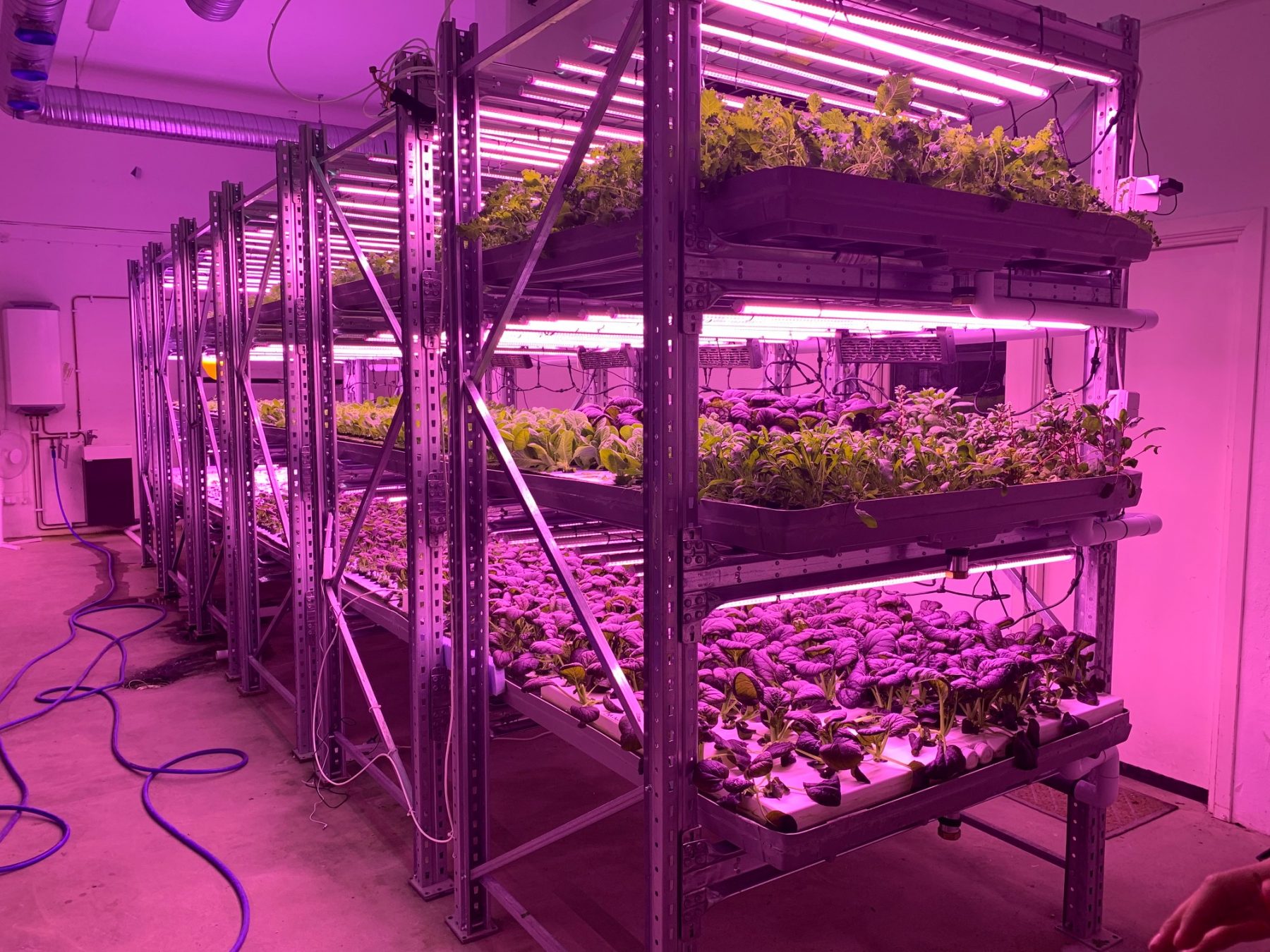
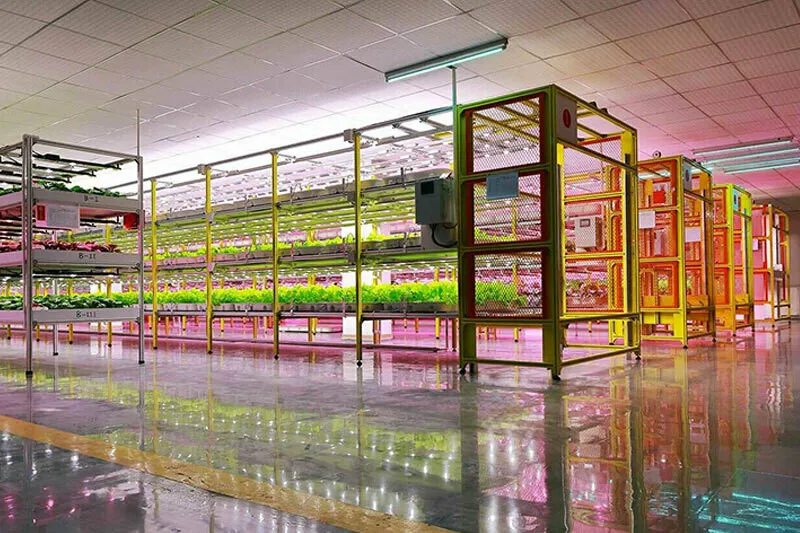
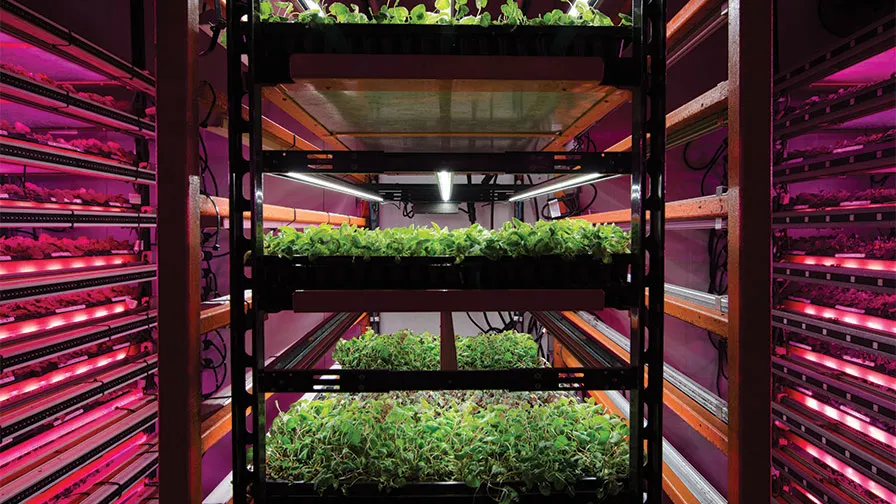
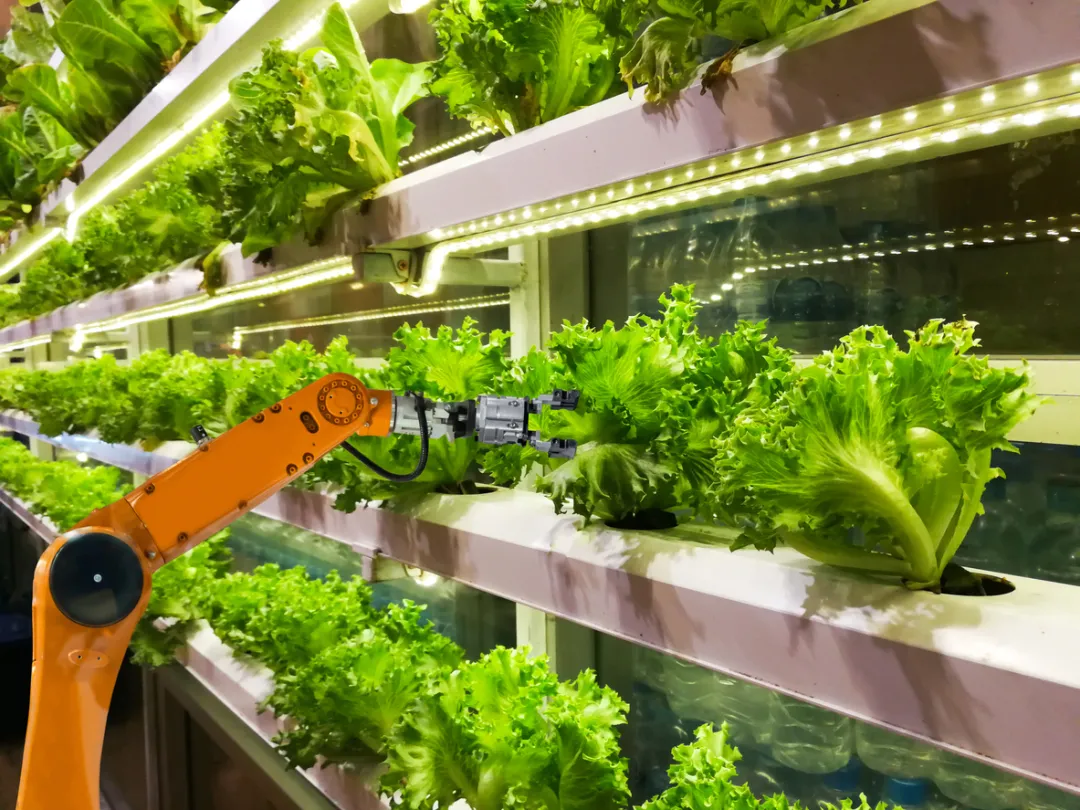
The plant factory is a high-efficiency facility agriculture system that achieves annual continuous production of crops through high-precision environmental control in the facility. The computer automatically controls the temperature, humidity, light, CO2 concentration, and nutrient solution during the growth of crops. A brand-new production method that is not or seldom restricted by natural conditions. Plant …
More -
Ultraviolet (UV) Plant Photobiology
Ultraviolet rays refer to light with a wavelength of less than 400m, accounting for 7% of solar radiation. High-intensity ultraviolet light less than 300mm is harmful to plants, and ultraviolet light less than 280m can kill plants. 320~340nm has little effect on plant cryptochrome. Sunlight is a continuous spectrum with wavelengths ranging from 100nm X-rays …
More -
The light quality requirements of plants-the research and development direction of light parameters of grow lights
Light is a key environmental element for plant growth and agricultural production. Photosynthesis is the main source of inorganic-organic transformation of materials on the earth. The wavelength in the range of 300mm to 800mm can be absorbed by green plant chlorophyll or photoreceptors. Around the world, before the 1970s, because there were only electric light …
More -
The core parameters of LED grow lights
Photosynthetic Active Radiation (PAR) The radiation of a specific wavelength range (400-700nm) used by plants for photosynthesis is called photosynthetically active radiation, and there are two labeling units: One is expressed in photosynthetic irradiance (w/m2), which is mainly used for generalized research on photosynthesis of sunlight. The second is expressed by the photosynthetic photon flux density …
More