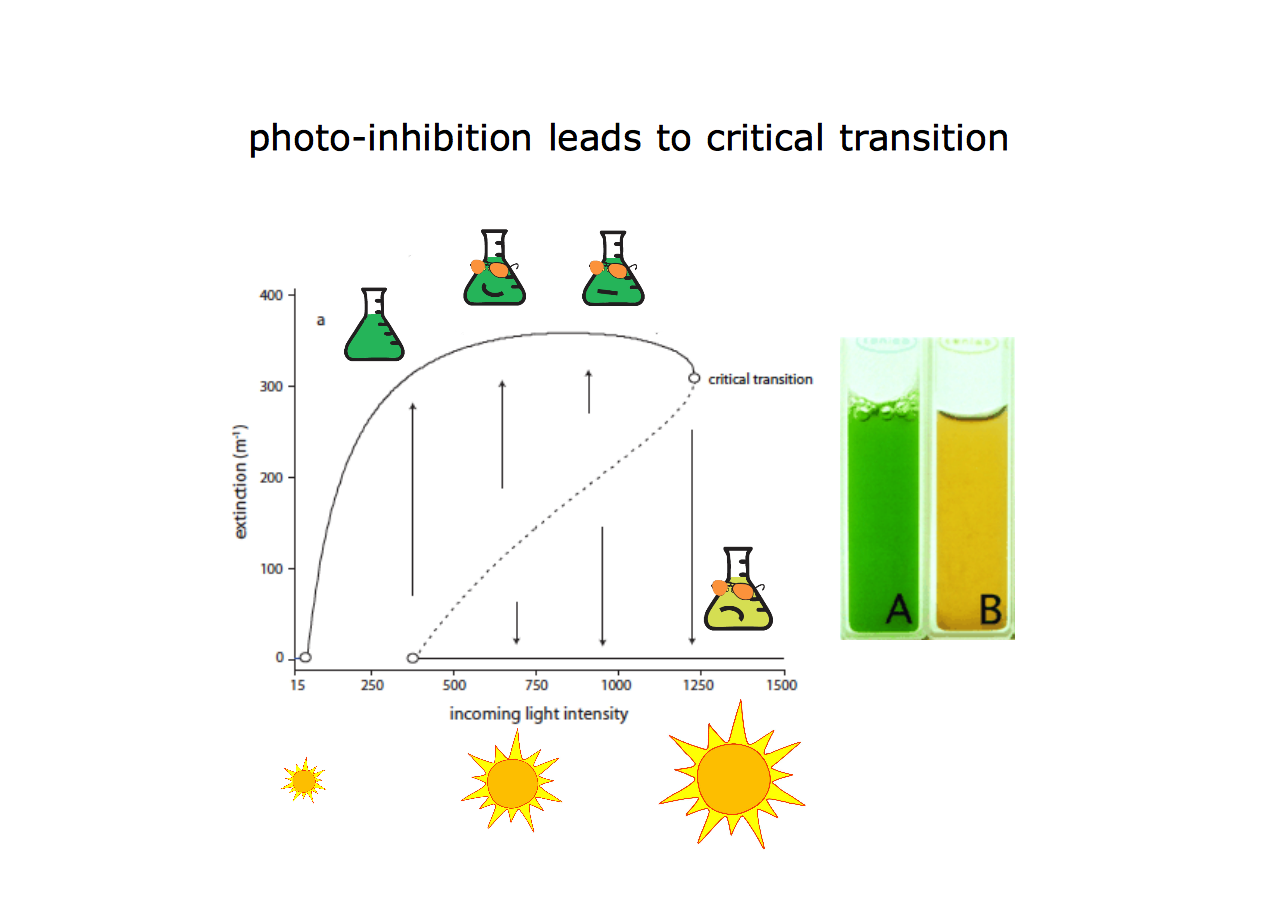
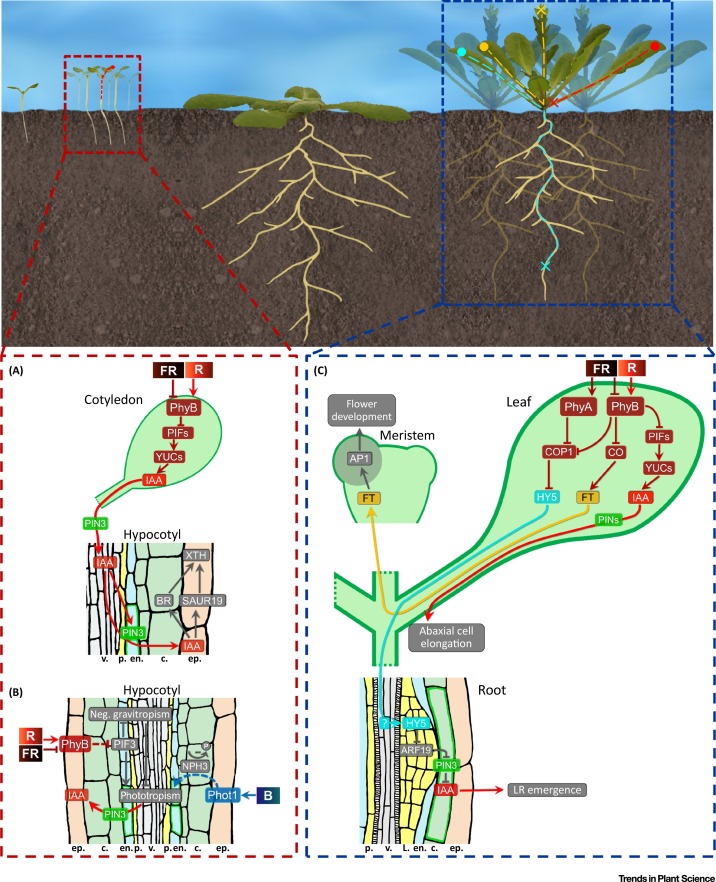
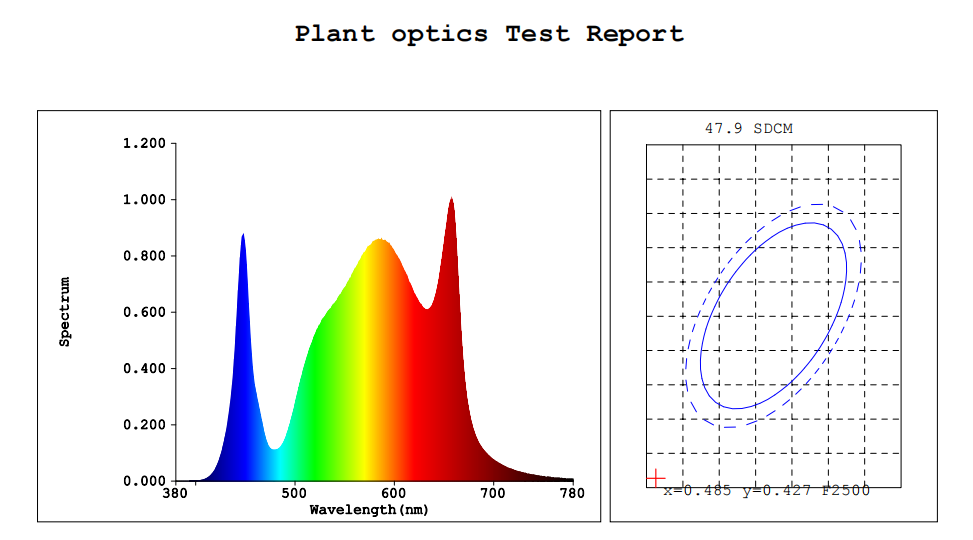
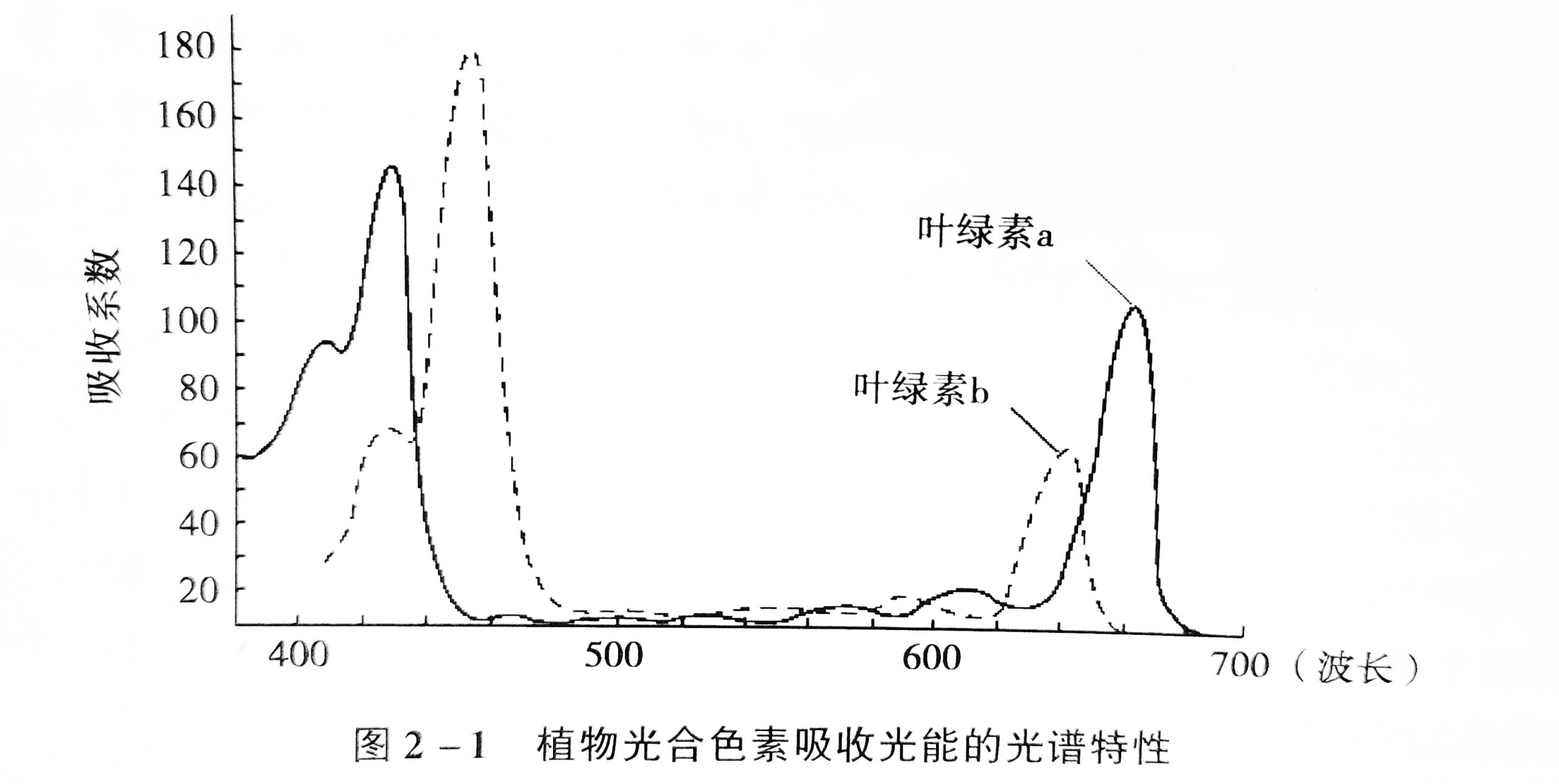
photoinhibition Photoinhibition occurs when light energy exceeds the demand for photosynthesis. The basic feature of photoinhibition is the reduction of photosynthetic efficiency (quantum efficiency of photosynthetic carbon assimilation and photochemical efficiency of photosystem II). According to the difference in the recovery speed of photosynthetic efficiency after the removal of photoinhibitory conditions, it can be divided …
More-
Typical state of plant photosynthesis(二)
-
Typical state of plant photosynthesis(一)
photoresponse When the photosynthetic apparatus (leaves, mesophyll cells, protoplasts or chloroplasts) is transferred from darkness to light, or from weak light to strong light, their photosynthetic rate goes through a long or short step-up process After that, a stable high level, the steady state level, is reached, a phenomenon known as the light-induced phenomenon of …
More -
Photosynthesis process
Photosynthesis occurs on the inner thylakoid membrane in the chloroplast of plants. Photosystem I and photosystem II are embedded in the thylakoid membrane, which is called the photosynthesis unit. It is composed of light-harvesting pigments composed of 200-300 antenna pigments. It is composed of body (absorbing light energy) and reaction center (consisting of 1 chlorophyll …
More -
The concept of plant photosynthesis
Photosynthesis refers to the process in which plant cells and bacteria containing photosynthetic pigments absorb light energy, assimilate inorganic matter into organic matter and release oxygen. The significance of photosynthesis is: ① convert inorganic matter into organic matter; ② convert light energy into chemical energy; ③ maintain the balance of oxygen and carbon dioxide concentrations …
More -
plant psychology
In 1966, an intelligence expert named Baxter imaginatively tied a polygraph to the leaves of an Arranthus when he was watering the garden flowers and plants, and wanted to test how fast the water rose from the roots to the leaves. . Later, he was surprised to find that the polygraph showed that the curve …
More -
Light environment regulation target and quality physiology of artificial light vegetable production
Quality and accumulation level of functional substances are one of the important indicators of facility vegetable production. For vegetables, the main nutritional quality indicators include primary metabolites (sugar, protein, minerals, vitamins, cellulose, etc.) and secondary metabolites (anthocyanins, phenolics, yellows, lycopene, etc.) . These indicators are controlled by lighting conditions, and are nutritional quality indicators that …
More -
The regulating effect of UV on the quality of facility plants
Hoffmann et al. (2015) found that PAR intensity plays an important role in the adaptation of plants to UV radiation. Therefore, the special morphological and physiological characteristics affected by strong light are also affected by blue light. The author believes that a larger amount of blue light in the spectrum is beneficial to the ability …
More -
The regulation of UV on the growth and quality of facility plants
Due to the absorption of covering materials in greenhouses and greenhouses, the ultraviolet part of sunlight will be greatly reduced. An important feature of the greenhouse growth system is the lack of mid-wave ultraviolet UV-B (280~320nm) in natural sunlight. The physiological effects of this phenomenon are unclear. Plants often develop a thick leaf epidermis or …
More -
Distribution characteristics of ultraviolet light in plant factories
The plant factory is a high-efficiency facility agriculture system that achieves annual continuous production of crops through high-precision environmental control in the facility. The computer automatically controls the temperature, humidity, light, CO2 concentration, and nutrient solution during the growth of crops. A brand-new production method that is not or seldom restricted by natural conditions. Plant …
More